Getting Started
Register a MBean
Annotate your class with the @MBean annotation.
@MBean("GettingStarted:name=Person")
public class Person
{
...
}
Create an instance of your class and register it.
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Person person = new Person();
MBeans.registerMBeanFor(person);
}
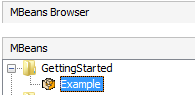
The program above will register and export the given person object as an MBean:
Adding Attributes
To export fields of a class as MBean attribute simple annotate it as @MAttribute
@MBean("GettingStarted:name=Person")
public class Person
{
@MAttribute
private String firstName = "Reto";
}
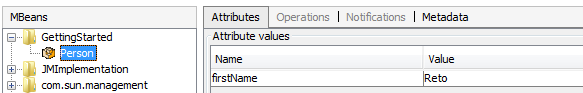
The field is then available as read only attribute in the MBean:
Writable Attributes
To make a MBean writable set the MAttribute parameter isWritable to true:
@MBean("GettingStarted:name=Person")
public class Person
{
@MAttribute(isWritable=true)
private String firstName = "Reto";
}
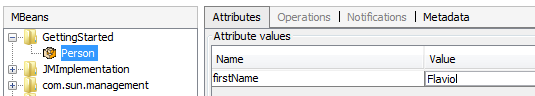
Now the MBean attribute can be changed. Changing the attribute in the MBean will also change the value of the field in the person object:
Adding Operations
To export a method of a class as a MBean operation simple annotate it with @MOperation
@MBean("GettingStarted:name=Person")
public class Person
{
private String firstName = "Reto";
@MOperation
private void print()
{
System.out.println(firstName);
}
}
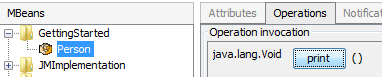
The operation of the MBean can now be executed and the annotated method will be called:
EL Like Expressions
To export more than one object of the same class as MBean the object’s name must be unique. Use EL like expressions to give each object a unique name:
@MBean("GettingStarted:type=Person,name=#{firstName}")
public class Person
{
private String firstName;
public Person(String firstName)
{
this.firstName = firstName;
}
Create two different Person objects with different first names and register them as MBeans:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Person reto = new Person("Reto");
MBeans.registerMBeanFor(reto);
Person flavio = new Person("Flavio");
MBeans.registerMBeanFor(flavio);
}
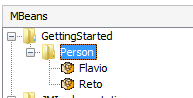
There are now two MBean with different names registered:
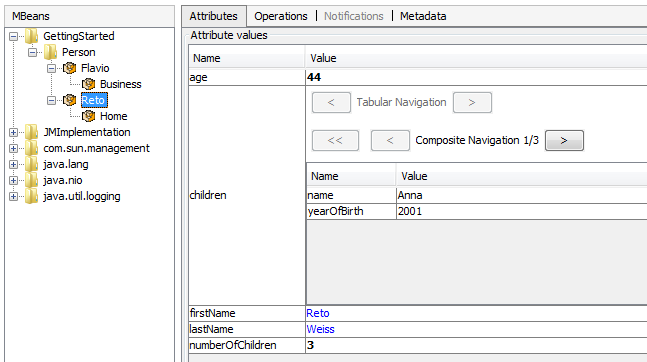
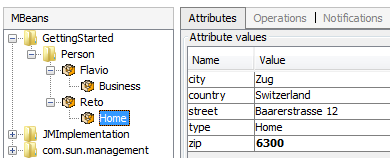
Enhanced Example
The following enhanced example uses some advanced annotations:
- The @MInclude annotation can be used to add attributes and operations that are declared on an other class to the current MBean.
- The @MCompositionReference can be used to reference another MBean that is also registered/unregistered if the current MBean is registered/unregistered.
- The @MSizeAttribute can be used to add an attribute that contains the size of a List or Map or the length of a String.
@MBean(value = "GettingStarted:type=Person,name=#{firstName}", description = "This is #{firstName} #{name} living in #{home.city}")
public class Person
{
private String firstName;
@MAttribute(name = "lastName", description = "Last name of the person", isWritable = true)
private String name;
// The @MInclude annotation can be used to add attributes and operations that are declared on an other class to the current MBean.
@MInclude
private Age age;
// The @MCompositionReference can be used to reference another MBean that is also registered/unregistered if the current MBean is registered/unregistered.
@MCompositionReference(concatName = true)
private Address home;
@MAttribute
// The @MSizeAttribute can be used to add an attribute that contains the size of a List or Map or the length of a String.
@MSizeAttribute(name = "numberOfChildren")
private List<Child>; children;
public Person(String firstName, String name, Age age, Address home, List<Child> children)
{
this.firstName = firstName;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.home = home;
this.children = children;
}
@MAttribute(description = "First name of the person", isWritable = true)
public String getFirstName()
{
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName)
{
this.firstName = firstName;
}
@MOperation(description = "Prints the firstName and lastName to system out", impact = Impact.INFO)
public void print()
{
System.out.print(firstName);
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.println(name);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
PersonRegistry registry = new PersonRegistry();
Person reto = new Person("Reto", "Weiss", new Age(LocalDate.of(1972, 6, 10)),
new Address("Home", "Baarerstrasse 12", 6300, "Zug", "Switzerland"),
Arrays.asList(new Child("Anna", 2001), new Child("Toni", 2003), new Child("Gisela", 2007)));
registry.addPerson(reto);
Person flavio = new Person("Flavio", "Sadeghi", new Age(LocalDate.of(1986, 7, 23)),
new Address("Business", "Baarerstrasse 12", 6300, "Zug", "Switzerland"),
Arrays.asList(new Child("Mirco", 2013)));
registry.addPerson(flavio);
}
}
public class Age
{
private LocalDate birthday;
public Age(LocalDate birthday)
{
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@MAttribute(description = "Age in years of the person")
public int getAge()
{
return birthday.until(LocalDate.now()).getYears();
}
}
@MBean(value = "address=#{type}", description = "A postal address")
public class Address
{
@MAttribute
private String type;
@MAttribute
private String street;
@MAttribute
private int zip;
@MAttribute
private String city;
@MAttribute
private String country;
public Address(String type, String street, int zip, String city, String country)
{
this.type = type;
this.street = street;
this.zip = zip;
this.city = city;
this.country = country;
}
}
The MCollections class provides methods to convert collections to managed collections. A managed collection automatically registers MBeans that are added to the collection and unregisters them if they are removed.
public class PersonRegistry
{
// Every person put to these collection will be registered as MBean!
private Map<String, Person> persons = MCollections.managedMap(new HashMap<>());
public void addPerson(Person person)
{
persons.put(person.getFirstName(), person);
}
}
- The annotation @MComposite declares a complex attribute type.
- The @MItem annotation is used to add properties to the complex type.
// The annotation @MComposite declares a complex attribute type
@MComposite
public class Child
{
// The @MItem annotation is used to add properties to the complex type.
@MItem(description = "Name of the child")
private String name;
@MItem(description = "Year of birth of the child")
private int yearOfBirth;
public Child(String name, int yearOfBirth)
{
this.name = name;
this.yearOfBirth = yearOfBirth;
}
}
The example will create the following MBeans: